In HVLS ceiling fan applications, inner rotor motors and outer rotor motors each have their own advantages and disadvantages. The following is a detailed comparison of the two to help you better understand their differences:
________________________________________
1. Efficiency and energy consumption
• Inner rotor motor:
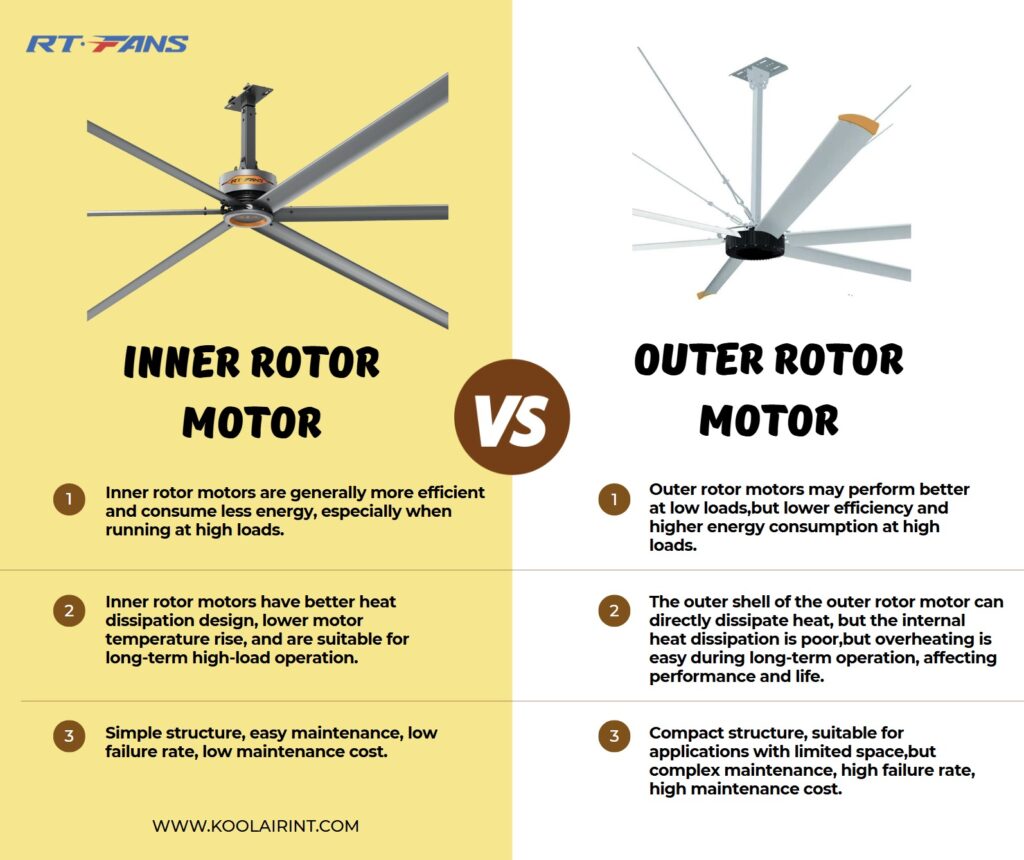
o Advantages: Inner rotor motors are generally more efficient and consume less energy, especially when running at high loads.
o Disadvantages: No significant disadvantages.
• Outer rotor motor:
o Advantages: Outer rotor motors may perform better at low loads.
o Disadvantages: Lower efficiency and higher energy consumption at high loads.
________________________________________
2. Heat dissipation performance
• Inner rotor motor:
o Advantages: Inner rotor motors have better heat dissipation design, lower motor temperature rise, and are suitable for long-term high-load operation.
o Disadvantages: No significant disadvantages.
• Outer rotor motor:
o Advantages: The outer shell of the outer rotor motor can directly dissipate heat, but the internal heat dissipation is poor.
o Disadvantages: Overheating is easy during long-term operation, affecting performance and life.
________________________________________
3. Structure and maintenance
• Inner rotor motor:
o Advantages: Simple structure, easy maintenance, low failure rate, low maintenance cost.
o Disadvantages: No significant disadvantages.
• Outer rotor motor:
o Advantages: Compact structure, suitable for applications with limited space.
o Disadvantages: Complex maintenance, high failure rate, high maintenance cost.
________________________________________
4. Noise level
• Inner rotor motor:
o Advantages: Low noise during operation, providing a quieter working environment.
o Disadvantages: No significant disadvantages.
• Outer rotor motor:
o Advantages: No significant advantages.
o Disadvantages: Due to structural reasons, the noise is high during operation, which may affect working comfort.
________________________________________
5. Adaptability and reliability
• Inner rotor motor:
o Advantages: Strong adaptability to the environment, suitable for harsh working conditions such as high temperature, high humidity, dust, etc., and high reliability.
o Disadvantages: No significant disadvantages.
• Outer rotor motor:
o Advantages: No significant advantages.
o Disadvantages: Performance degradation or failure is likely to occur in harsh environments, affecting production efficiency.
________________________________________
6. Cost and cost performance
• Inner rotor motor:
o Advantages: Lower overall running cost, more economical in long-term use, and high cost performance.
o Disadvantages: No significant disadvantages.
• Outer rotor motor:
o Advantages: Better initial performance.
o Disadvantages: Higher maintenance and replacement costs, and overall cost performance is not as good as that of inner rotor motors.
________________________________________
7. Technology maturity
• Inner rotor motor:
o Advantages: Mature technology, high reliability after years of market verification.
o Disadvantages: No significant disadvantages.
• Outer rotor motor:
o Advantages: Advantages in certain specific applications.
o Disadvantages: The technology is not yet fully mature, and there may be risks in long-term use.
________________________________________


